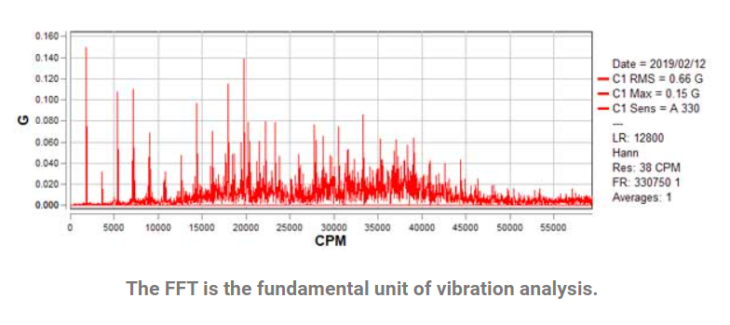
The FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) is a mathematical calculation intended to decompose a signal into all its frequencies. FFT chart provides the possibility to diagnose faults based on frequencies and evaluate the intensity of each one of them based on the amplitude.
Vibration Measurement parameters
Vibration Analysis techniques identify 3 major measurement parameters. Each one of these parameters gives particular importance to certain ranges of frequencies.
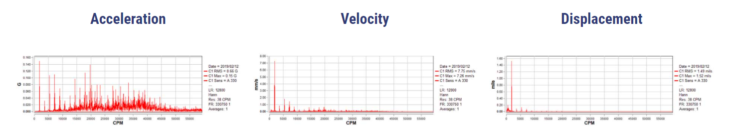
Acceleration gives higher importance to high frequencies. It is useful to see bearing condition.
Velocity gives equal importance to high and low frequency. It is related to the destructive force of the vibration and therefore the most important unit available.
Displacement prefers low frequencies. It is useful for during dynamic balancing, orbits and ODS (Operating Deflection Shapes).
Observe the spectra below. They all belong to the same signal. Notice that you will see peaks at the same frequencies, but with different amplitudes in each one of them. Additionally observe how every parameter assigns different importance to frequency ranges.
Maintenance plans
Vibration Analysis in corrective maintenance aims to diagnose and correct an existing vibration problem.
On the contrary, in predictive maintenance the objective is to predict faults generating trending the vibration and identifying its behavior over time.
Can Vibration Analysis predict failures? – Predictive Maintenance
Yes, in most cases at least, we can predict failures. Let’s make an analogy.
Did you ever take your car to the mechanic because you noticed a new noise, or because a noise that was already there is getting louder?
Unconsciously by taking this decision you are predicting a failure. You know that if you do not take the car to the mechanic the car will eventually leave you stranded. And that is your prediction. In predictive maintenance the principle is the same, but unlike cars, we are not always close to the machines to be able to hear the noises or feel the vibrations, not to mention most of them are inaudible. Therefore, vibration analyzers accurately trend the amplitude of these “noises”, and even better, they are capable of identifying the source of this raising “noise”.
Proactive maintenance
Proactive maintenance is a new trend that aims to not only predict downtimes, but it also accurately specifies the failures that will cause them.
There are several approaches for this, but they are all based fundamentally on tracking which frequencies are responsible in vibration changes. A normal spectrum usually has 400 to 200,000 points, and tracking over time every single one is complicated.
Octave Bands are simplified FFT spectra with a standard number of lines, usually between 8 and 32. In this way, octave bands are very useful for tracking small amount of segments of FFT over time. Hence, identifying faulty components is much easier.

Vibration Analyzers
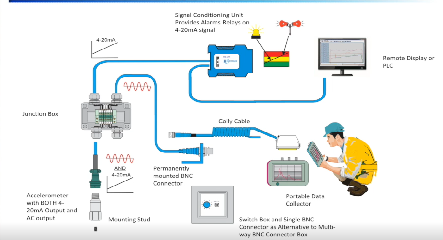
New generation of vibration analyzers have evolved with easy to use complex features like 3D simulations or GearBox analysis. Additionally these analyzers integrate millions of resolution lines and automated routes recording making our lives much easier.
Wireless Accelerometers
The new era of technology has allowed wireless accelerometers to communicate with almost any device such as smartphones and tablets. Despite the big bandwidth these wireless triaxial accelerometers require, they are capable of sending 3-axis simultaneously in real time and even with the possibility of adding a fourth channel for phase analysis and balancing.
IOT Internet of Things in Vibration analysis
Devices with a size of a golf ball are now capable of sending vibration wirelessly for 3 to 6 years without changing the battery. By only gluing the base and configure it in the software you will be all set to start analyzing through the cloud or directly in your Smartphone. Additionally, this technology now also includes temperature sensors, RPM current and many others that integrate new parameters within the same analysis.
Vibration analysis Cloud
New web technology and progress in telecommunications now allow us to send recorded data on Smartphones or through IOT devices to the cloud in order to automate them and share them with distant expert analysts for further analysis.
In the Same way, cloud based vibration analysis allows us to easily share information with the end user to facilitate decision making. Automated reporting are now available with customizable tools that allow users to see exactly what they need.
Cloud based maintenance is a tendency just like everywhere else in our lives.
Learning now from cloud-based vibration analysis systems is very important since it will become more and more complex.
Learning algorithms in vibration analysis
New algorithms for self-learning machinery patterns are growing and becoming more popular. These algorithms measure RMS values over a period of time to then evaluate which range of values is normal for that particular machine. Hence these systems are able to inform whenever the vibration of the machine exceeds the maximum.
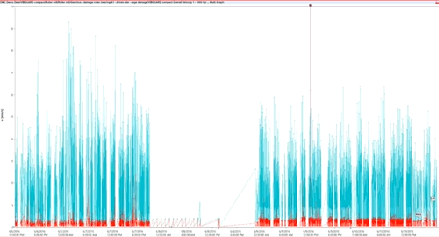
Another way of learning is by creating automatically an envelope alarm over an average of FFTs (see picture). After defining a normal envelope limit, the systems are able to detect whenever a particular frequency on the spectrum reaches a limit.
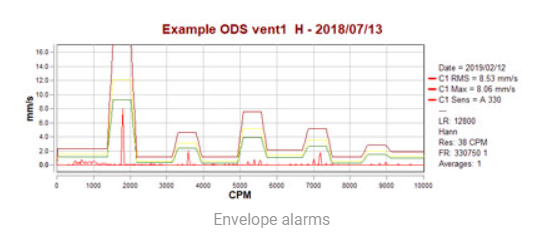
These algorithms are already making vibration analysis much easier leaving tough tasks to computers. These systems significantly reduce the workload for vibration analysts and allow them to focus on things that really deserve their time.
Learning algorithms in vibration analysis
Definitely, these new technologies will greatly change the way we see vibration analysis today. Not only will they make life easier for us in terms of routine work, but they will also allow our knowledge to grow even more in terms of vibrations and their relationships with other parameters.
The sooner we adopt these technologies the longer we will have to learn their potential. Adapting our way of thinking is crucial in this environment that changes with such speed.
Summary